Common Types of Evaporators and Their Applications
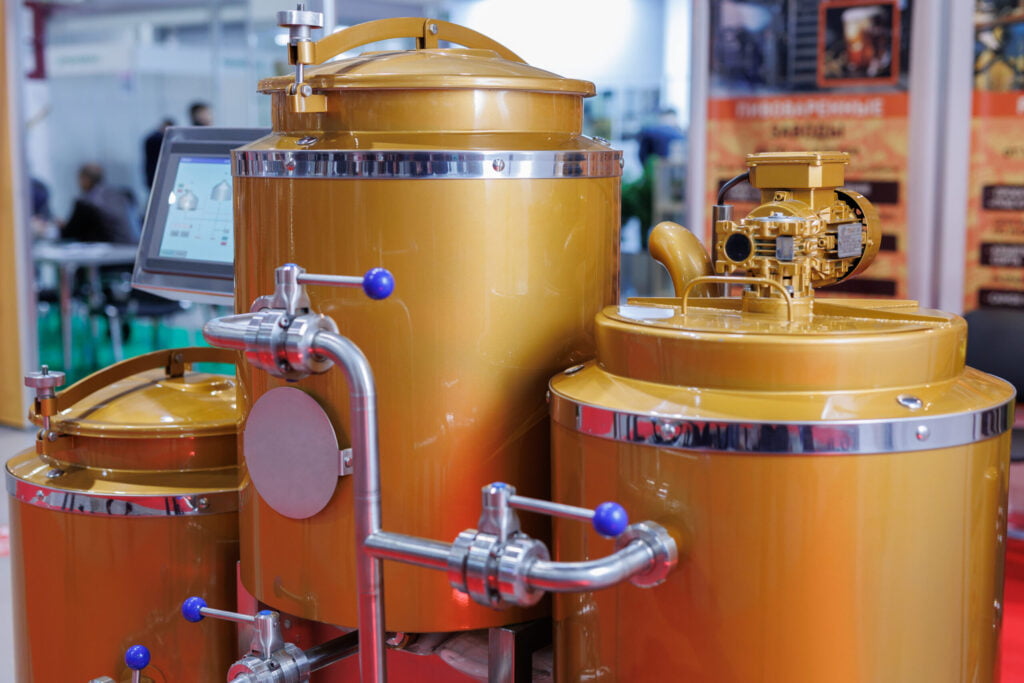
Evaporators are vital components in several industrial systems, essential for processes such as concentration of solutions, recovery of solvents, and conditioning of products. Understanding the different types of evaporators and their applications can lead to more efficient and effective operations in a range of industries. This comprehensive guide aims to acquaint readers with the most commonly used evaporators and their functions. Below, we delve into several key types and their applications in various industries.
Understanding the Basics of Evaporators

The fundamental purpose of an evaporator is to convert the liquid form of a chemical solution into its gaseous form, most commonly through the use of heat. In industrial setups, evaporators play a pivotal role in concentrating substances, purifying solutions, and recovering solvents.
Evaporators come in different shapes and sizes, and their designs vary based on the specific application requirements. Generally, their design is to facilitate the optional use of heat, minimize energy use, and ensure a safe operation.
The category of industrial evaporators is extensive, and each type possesses unique features that make it suitable for specific applications. Some equipment like evaporators are designed to be highly versatile to fit a range of industries.
Understanding the specifics and intricacies of different types of evaporators is key to utilizing these powerhouses of the industry to their full potential.
The Significant Role of Natural Circulation Evaporators
Natural circulation evaporators operate on the principle of density differences within the liquid, which causes the lighter fractions to rise and heavier fractions to settle. This natural circulation process eliminates the need for mechanical pumps, reducing operational costs.
These evaporators are desirable in a range of industrial applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Among the most common applications are the concentration of food and dairy products, sugar solutions, and chemical mixtures.
However, they also have some limitations, such as the potential for scaling, relatively low thermal efficiency, and the likelihood of product degradation due to prolonged exposure to heat.
Despite these drawbacks, natural circulation evaporators continue to be a popular choice in various industries due to their advantages.
Gaining Insight Into Forced Circulation Evaporators
Unlike natural circulation evaporators, forced circulation evaporators utilize a mechanical force to pump the liquid and create a controlled circulation of the fluid. This feature makes them preferable for handling thick, viscous materials and products prone to crystallization or scaling.
Forced circulation evaporators offer better control over residence time, a lower risk of scaling, and a generally superior thermal performance. Their industrial applications are numerous, ranging from the food processing industry to wastewater management.
The downside to forced circulation evaporators includes greater energy requirements, higher operating costs, and more complex maintenance due to the presence of pumps and moving components.
Despite these challenges, forced circulation evaporators can provide significant process benefits in certain applications, particularly where product quality and consistency are critical.
Crucial Applications of Plate Type and Film Type Evaporators
Plate-type and film-type evaporators offer efficient and economical solutions for several key industrial applications. Plate-type evaporators, in particular, provide compact and efficient heat transfer, making them suitable for applications that require low operating temperatures and short residence times.
Film-type evaporators, on the other hand, are ideal for heat-sensitive products, owing to their operation at low temperatures and ability to produce high product concentrations without degrading the product. They find extensive application in the food and beverage industry, as well as the pharmaceutical sector.
While these types of evaporators offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges like mechanical complexity, greater energy usage, and sometimes, more rigorous maintenance protocols. But, their ability to deliver high-quality results often outweighs these constraints.
With a proper understanding of the operating principles and potential applications, these types of evaporators can be strategically employed to boost overall operational efficiency.
Altogether, evaporators play a significant role across a variety of industries. Their versatility and effective functioning make them a valued part of many industrial processes. Each type offers unique advantages and has the potential to boost productivity and quality when appropriately applied.




